Helping Reduce Symptoms for a Healthier Life
Asthma involves a chronic or long-term lung disease that results in swelling in the airways. It also causes the narrowing of the bronchial tubes, called bronchoconstriction. Some people also develop excess mucus production.
Although there is currently no cure for asthma, there are asthma treatments that help reduce symptoms. But it is important to understand what type of medication or treatment targets which symptoms.
What Signs and Symptoms of Asthma Require Treatment?
Everyone has their own unique experience with asthma symptoms. It is essential to work with your doctor to develop an asthma action plan. An action plan provides information and direction on when to use which type of asthma medication. This helps prevent symptoms and the frequency of flare-ups.
In general, if you develop asthma symptoms, it is usually best to follow your action plan and take medications as prescribed.
Typical signs and symptoms that require using asthma medication include:
- Wheezing.
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest tightness.
- Coughing.
The signs above may vary in severity. Even if symptoms are mild, you should not wait for treatment. Letting an asthma attack go without treatment can lead to worsening symptoms.
What Can You Do for Quick Relief of Asthma?
One of the best treatments for asthma is quick-relief medications; they differ from asthma maintenance drugs. Quick-relief asthma medications work fast to stop or reduce symptoms. The most common quick-relief medications include fast-acting bronchodilators.
This class of medication works by relaxing the smooth muscle tissue around the airways. As the medication relaxes the smooth muscles, the airways widen or dilate. This reduces wheezing and makes getting air in and out of the lungs easier.
Quick-relief medications work fast. But in some cases, multiple doses are needed every few hours to keep symptoms at bay during an attack.
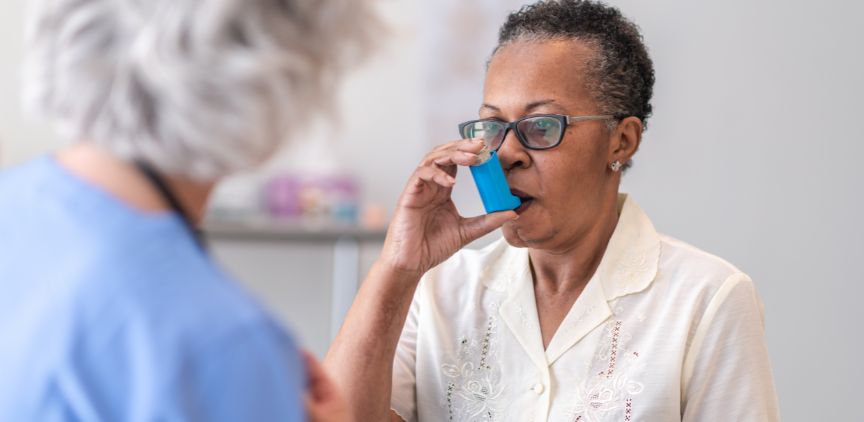
Usually, for quick relief, someone takes a bronchodilator in the form of an inhaler. An inhaler is quick and easy, and it delivers medications directly to the lungs. Another option is taking a bronchodilator through a nebulizer, called a breathing treatment.
A nebulizer uses a special machine to turn liquid medication into an aerosol or mist that you inhale.
Common bronchodilators for quick relief include Xopenex, albuterol, and Atrovent. Common side effects from using quick-relief medications include an increased heart rate, headache, and anxiety.
How do you Treat Severe Asthma?
A severe asthma attack causes the same symptoms, such as wheezing and trouble breathing. But symptoms may become more intense and do not immediately respond to quick-relief medications.
If you develop severe asthma, it is vital to seek medical help. Severe asthma may require the following treatment:
Continuous breathing treatments: With severe asthma, one dose of an inhaler or a breathing treatment may not control symptoms. A continuous breathing treatment involves inhaling bronchodilators for an hour or two. This type of treatment usually requires monitoring to ensure side effects, such as increased heart rate, do not become significant.
Steroids: Steroids reduce inflammation in the airways. The inflammation, along with the narrowing, makes it hard to breathe. Bronchodilators treat airway narrowing, and steroids target airway swelling.
Steroids are given through inhaled medications, orally, or intravenously in severe asthma attacks.
Airway support as needed: In severe asthma, it can become difficult to breathe. If that occurs, someone may require oxygen to improve blood oxygen levels. In the most serious cases, breathing assistance using a mechanical ventilator may be needed until symptoms improve.
Other Asthma Treatment Tips
You can also do some additional things to manage asthma effectively and reduce the frequency of flare-ups and severity of symptoms. Consider the following tips:
Learn what triggers an asthma attack: Keep a log of what symptoms you develop and what activities you are doing. It may help you connect the dots and determine what triggered symptoms. Once you know your triggers, you can take steps to limit them.
Get to a healthy weight: According to the American Lung Association, people that are obese develop asthma at higher rates than people at a healthy weight. They also take more asthma medication and have a harder time controlling symptoms. If you are overweight, talk with your doctor about safe ways to shed some pounds.
Talk to your healthcare provider about asthma maintenance medication: Depending on the severity of asthma symptoms, you may need to take maintenance medication. For example, combination medications that contain a long-acting bronchodilator and a steroid may help prevent symptoms. Long-acting bronchodilators prevent airway constriction for several hours. When you combine this type of medication with a steroid, it can reduce the frequency of asthma attacks.
Consider attending an asthma education program: Asthma education programs are often available through hospitals and community centers. Asthma can become a complex condition that requires a comprehensive management plan. Learning as much as possible about treatment options helps you manage the disease more effectively.